pywasp.wasp.get_climate#
- pywasp.wasp.get_climate(output_locs, stab_source='ERA5', baro_source='ERA5', interp_method='nearest')[source]#
Get climatological parameters interpolated to the output locations
Warning
This function is experimental and its signature may change
- Parameters:
output_locs (
xarray.Dataset) – Spatial dataset (point, stacked_point, or cuboid) with the output locations to interpolate tostab_source (
str,xarray.Dataset,None) – String indicating which data source should be used for the stability information. If it is a xarray.Dataset, this is used as a stability source. If it is set to None, it means a dataset with dummy values is returned. by default ‘ERA5’, the only available value for now.baro_source (
str,xarray.Dataset,None) – String indicating which data source should be used for the baroclinicity parameters. If it is a xarray.Dataset, this is used as a baroclinicity source. If it is set to None, it means a dataset with dummy values is returned. Available values are ‘ERA5’ and ‘CFSR’, defaults to ‘ERA5’.interp_method (
str) – Interpolation method to use. See windkit.spatial.interp_unstructured_like for available methods. Defaults to ‘nearest’
- Returns:
xarray.Dataset– Dataset with mean climatological parameters for the specified output_locs
Notes
This routine extracts two things from a prepared file with data:
the baroclinicity parameters
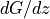 and
and 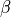
stability information (mean and standard deviation of the temperature scale and boundary layer height over land and sea)
The dgdz parameter represents the change of the geostrophic wind with height (s^-1), where as beta describes the direction in which the vector is pointing (0 for pointing towards the east). Assuming a boundary layer height of 1000 m
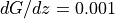 and
and 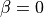 thus means that in a climatological sense the
geostrophic wind is increasing with 1 m/s from the ground to a 1000 m
from west to east. Further details on these parameters
and how they affect the wind modelling in Wasp is described
in [3]
thus means that in a climatological sense the
geostrophic wind is increasing with 1 m/s from the ground to a 1000 m
from west to east. Further details on these parameters
and how they affect the wind modelling in Wasp is described
in [3]In mountaineous terrain the geostrophic shear can get very large. When there is values of
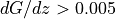 it is recommend to explore
the results also with the geostrophic shear turned off. There is also a
hard limit in the WAsP core which limits the geostrophic shear effect,
because the geostrophic drag law is not applicable for
it is recommend to explore
the results also with the geostrophic shear turned off. There is also a
hard limit in the WAsP core which limits the geostrophic shear effect,
because the geostrophic drag law is not applicable for 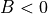 .
This is set in parameter 103 in
.
This is set in parameter 103 in Climate.The temperature scale represent the climatological mean effect of stability on the wind profile. In the standard profile model (which is set using
Climate.set_profile_model= 0 , the heat fluxes have default values specified in parameters 56-59 and have units of W/m^2. These values are the same for all wind direction sectors.If the
Climate.set_profile_model`= 2, it means that the stability information is specified as a mean and standard deviation of a temperature scale with units K (degrees). They can generally be obtained from reanalysis data or observations of kinematic heat fluxes. They will generally depend on wind direction and vary with wind direction.The boundary layer heights are not used in profile model 0 and 1, because h is specified to scale with
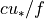 ,
where
,
where 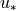 is the friction velocity,
is the friction velocity, 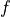 the coriolis parameter
and the scaling constant
the coriolis parameter
and the scaling constant  is specified with param(96). When
param(96)<0 one can explicitly set the boundary layer
height over land and sea using the values specified in the
mesoscale climate.
is specified with param(96). When
param(96)<0 one can explicitly set the boundary layer
height over land and sea using the values specified in the
mesoscale climate.The dataset is required to have the following variables:
- mean_temp_scale_landnumpy array
mean heat flux (W/m^2) or normalized heat flux (W m^-1 s^-1) over land
- mean_temp_scale_seanumpy array
mean heat flux (W/m^2) or normalized heat flux (W m^-1 s^-1) over sea
- rms_temp_scale_landnumpy array
standard deviation of heat flux or normalized heat flux over land
- rms_temp_scale_seanumpy array
standard deviation of heat flux or normalized heat flux over sea
- mean_pblh_scale_landnumpy array
mean boundary layer height over sea (m)
- mean_pblh_scale_seanumpy array
mean boundary layer height over sea (m)
- mean_dgdznumpy array
average magnitude of long-term mean geostrophic wind shear vector (s^-1)
- mean_dgdz_dirnumpy array
average direction of long-term mean geostrophic wind shear vector (degrees in mathematical coordinate system, i.e. zero for vector from west to east)

